First aid considerations for bowhunters: falls and broken bones
Bowhunters face many of the same outdoor survival and wilderness first aid situations that all outdoor users face. They should always be prepared for emergencies and have a basic understanding of first aid when going into remote areas.
Across the U.S. qualified people teach first aid. We strongly recommend you take a Red Cross or other recognized first aid course.
Heart attacks
If someone shows signs of a heart attack in the wild—chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, or dizziness—stop all activity immediately. Have the person sit, stay calm, and call for help using a phone, satellite messenger, or beacon. Monitor breathing and pulse; start CPR if they become unresponsive. Keep them warm, still, and reassured until help arrives. Avoid food or caffeine. Quick, calm, and prepared action can save a life.


Burns
If you or one of your hunting partners suffer a burn, here are steps to treat the wound:
- Place the burned area under cool (not cold) running water or gently apply a cool, wet compress until the pain eases.
- Remove rings or other tight items from the burned area if possible.
- Do not break any blisters. They help protect against infection.
- Apply lotion such as one with aloe vera. This helps prevent drying.
- Cover the burn with a clean bandage.
- If needed, take a nonprescription pain reliever.
Knife / broadhead cuts and bleeding
Most bleeding situations are caused by cuts. The best way to stop a cut from bleeding is by firmly applying pressure over the wound with a cloth or piece of clothing for a few minutes. However, if the cut is deep do not release the pressure because the bleeding will start again. If the injury is to the leg or arm keep it elevated.
Remember RED: Rest - Elevate - Direct pressure.


Snakebites
Snake bites should always be taken seriously, if not treated carefully and quickly, they can result in death.
- Call 911 immediately, get help as soon as you can, because even if the bite isn’t that painful initially, you still need to treat it as if it is potentially life-threatening.
- Wash the bite with soap and water.
- Keep the affected area still and lower than the heart in order to slow the spread of venom.
- Remove any jewelry or watches.
- Remain still and calm. Moving around will cause the venom to spread faster through the body.
- Cover the bite with a clean, dry bandage.
Embedded objects
Do not remove any embedded objects as it could lead to an even more serious injury. Pad the wound around the object firmly and go to the nearest hospital.

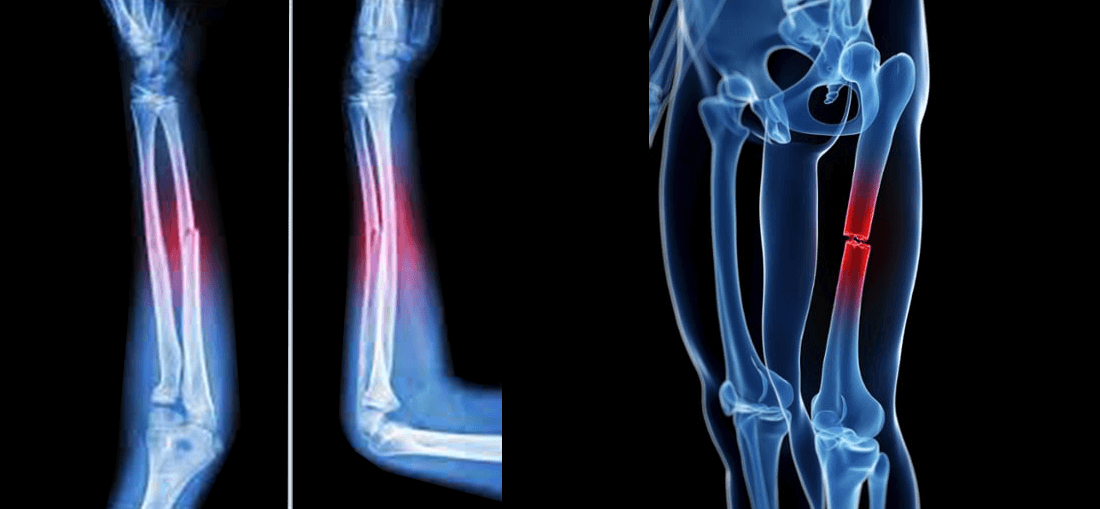
Broken bones
Hunting requires a lot of physical activity. Sometimes accidents, like broken bones, may happen.
- If necessary, stop any bleeding by applying pressure to the wound using a clean cloth, piece of clothing or bandage.
- Immobilize the injured area using a splint if possible.
- If available, administer anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen to reduce swelling and pain.
- Get medical help as soon as possible.
- Keep the victim calm, reassure them that help is on the way.
- Keep them alert and stay with them until medical assistance arrives.
Altitude
Altitude sickness is a condition that can happen when ascending to high altitudes too quickly. It is caused by lower air pressure and reduced oxygen levels at high elevations. The main symptoms include headache, dizziness, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea or vomiting, and difficulty sleeping.
The primary treatment for altitude sickness is descending to a lower altitude. You can also stop ascending and rest at the current altitude until symptoms improve. Taking medications or supplemental oxygen can also help relieve symptoms.
To prevent altitude sickness, ascend slowly, allowing time for your body to acclimate. Stay hydrated, avoid alcohol and sleeping pills, and consider taking preventive medication to avoid symptoms.


Allergies
Allergic reactions in outdoor settings can be triggered by various sources, including insect stings or bites, contact with certain plants, medications, or food allergens. The severity of these reactions can vary widely, from mild symptoms like itchy red spots on the skin to potentially life-threatening conditions characterized by difficulty breathing or loss of consciousness.
If someone experiences an allergic reaction, it is essential to keep them calm and still. If the person has prescribed medication, such as an inhaler for breathing difficulties or an epinephrine auto-injector for severe reactions, assist them in using it as directed. Regardless of the apparent severity, it is important to treat all allergic reactions seriously. In cases of severe symptoms or any doubt about the person's condition, immediate transportation to a medical facility is required to ensure proper treatment and prevent potential complications.
Shock
Shock can occur during hunting due to various factors such as severe injury, blood loss, or extreme stress. It is a life-threatening condition characterized by inadequate blood flow to vital organs.
Symptoms of shock include weakness, dizziness, pale and clammy skin, rapid breathing, fast but weak pulse, confusion, and decreased urine output.
When shock is suspected in a hunting scenario, immediate action is key. The first step is to call for emergency medical help. While waiting, lay the person flat on their back with legs elevated about 12 inches to improve blood flow to vital organs. Keep the person warm and comfortable, loosen any tight clothing, and do not give them anything by mouth. Control any visible bleeding by applying direct pressure.
Monitor breathing and pulse, being prepared to perform CPR if necessary. It is important to note that shock can worsen rapidly, so quick recognition and proper treatment are essential for the best chance of survival.