Wildlife Conservation Principles in the North American Model
What provides the set of guidelines principles for managing wildlife resources?
The principles of the North American Wildlife Conservation Model are explained more fully through a set of guidelines known as the Seven Sisters for Conservation.
What is wildlife conservation principles based on?
- Our fish and wildlife belong to all citizens and are to be managed in such a way that their populations will be sustained forever.
- Wildlife populations are sustained and scientifically managed by professionals in government agencies.
Population Inventory

Wildlife managers need to know two very important things - the amount of habitat available and how many animals live there. They must know about the quality of the available habitat and the animals that depend on it to survive.
Habitat mapping is an important tool for preserving wildlife habitat. Habitat maps indicate land ownership and how much habitat remains for different species in a given area. By looking at past trends and present land use practices, wildlife managers can plan programs to preserve wildlife habitat for the future.
Habitat inventories are fairly easy to obtain. Wildlife managers can study aerial photos and get information from landowners and forest managers. They can also go into the field and study the habitat.
It can be very difficult and expensive to actually determine how many animals live in an area. Wildlife inventories should include the age and sex ratios of the animals and how healthy the population is.
Much information for wildlife inventories comes from people in the field. We can all help wildlife managers by reporting what we see in the field. Hunters play an important role in this part of wildlife management.
Balance Animals and Habitat
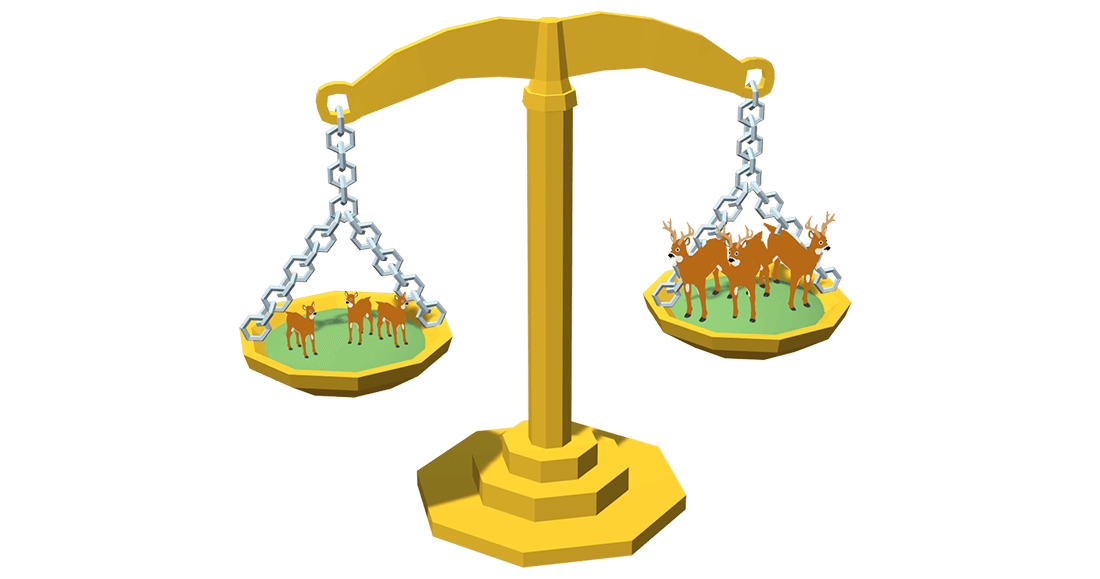

What is Carrying Capacity in hunting?
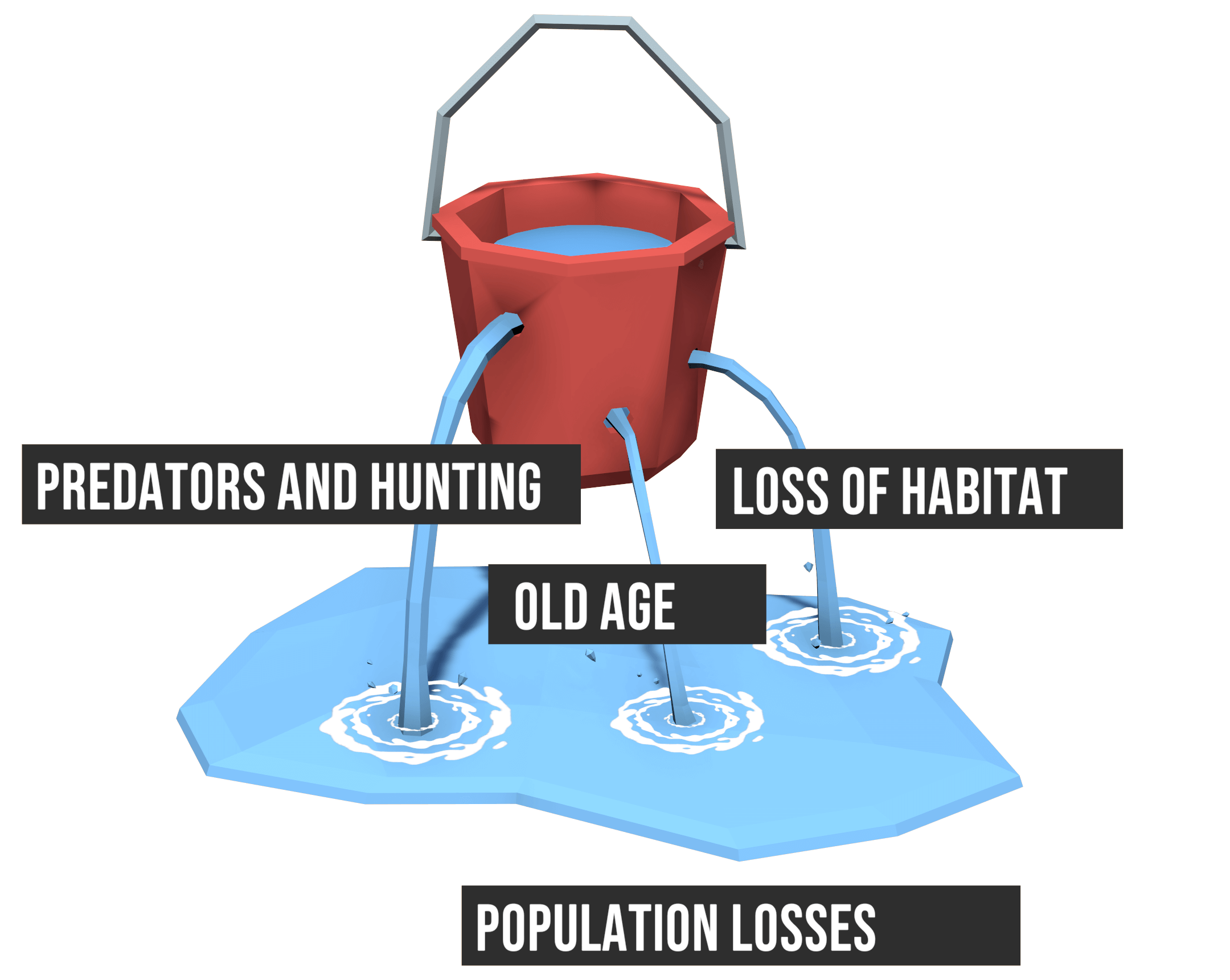
In an environment where there is no hunting, the animal population tends to increase until it reaches the carrying capacity and even surpasses it. When it is exceeded, it is the limiting factors such as predators, disease, the weather such as a harsh winter and the lack of food that will restore the balance. If, for example, there is a surplus of deer in a given territory, its food will become scarcer, the wolves will migrate toward the deer or because of such a high population the deer will start to develop diseases.
In an area where hunting occurs, the animal population is maintained at its carrying capacity and therefore fewer limiting factors appear which balances the livestock.
Wildlife managers will try to keep the number of animals using an area at a level that does not harm the land or vegetation. Each part of a habitat has a "carrying capacity" or number of animals that it will support. It is the goal of wildlife managers to balance the amount of wildlife with the available habitat.
What is biological surplus in hunting?
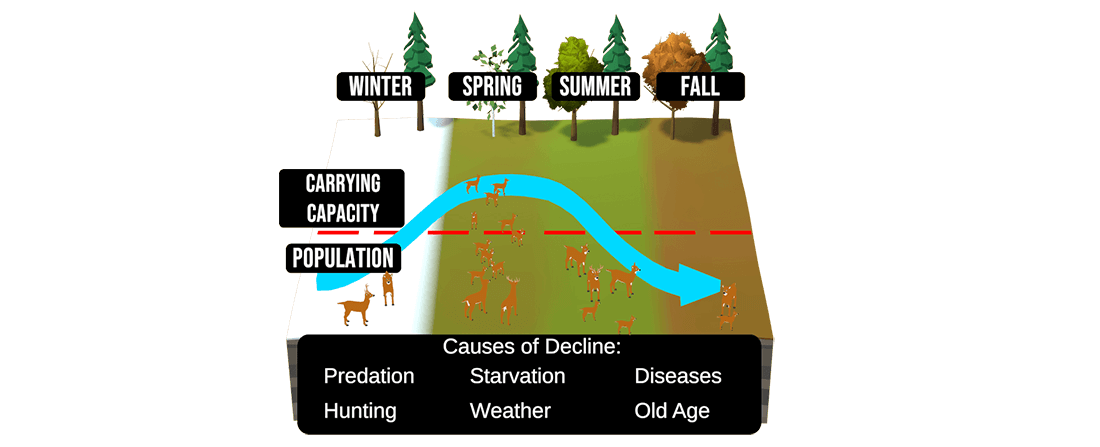
A biological surplus is the number of animals in a population beyond the carrying capacity. A biological surplus occurs when a species’ population becomes larger than the carrying capacity of its habitat. This may occur from:
- increased birth rates
- less predation
- lower mortality rates
- large scale migration
As a result, the overpopulated species as well as other animals in the ecosystem begin to compete for food, water, space, and resources.