Wildlife Identification
What wildlife characteristics should we consider when identifying game?
-
External features such as wings, feathers, and hide coloration
-
Skulls
-
Droppings
-
Tracks
-
Behaviors such as daily activity patterns
-
Habitat and range
Key characteristics of the animal
The size, shape, and color, are external features that can help us identify an animal. For example, many waterfowl species can be distinguished from each other by the pattern and coloration of the wings, especially the "bright showy" area of the wing called the speculum.
1. External Features
The size, shape, and color, are external features that can help us identify an animal. For example, many waterfowl species can be distinguished from each other by the pattern and coloration of the wings, especially the "bright showy" area of the wing called the speculum.
2. Skulls
Skulls of many animals have distinguishing characteristics such as crests, tooth types and patterns. Most skulls can be classified as herbivores or carnivores by the absence or presence of canine teeth or the number and type of molars. Carnivores are meat eaters and have well-developed canine teeth. Herbivores eat vegetation and lack well-developed canines. They usually have many well-developed molars and incisors.

3. Droppings
Droppings are another method of identifying species. Wild turkey droppings can even be used to determine sex. The club shaped droppings on the bottom are characteristic of gobblers while the corkscrew droppings are from a hen.
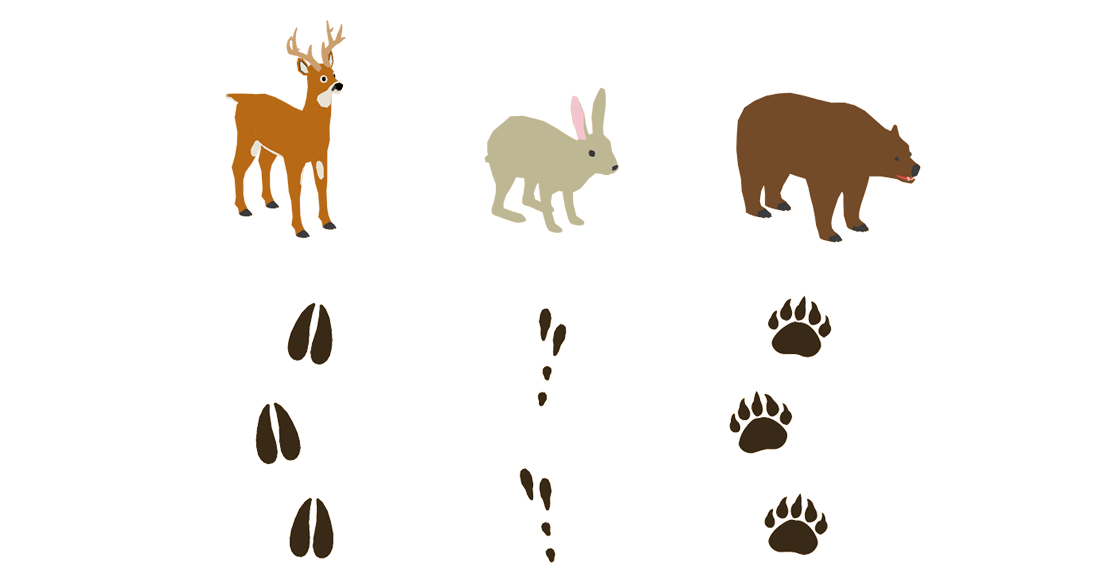
4. Tracks
When soil conditions are right, many species can be identified by their track imprint.
5. Behaviors
Knowing daily activity patterns such as whether the animals are nocturnal, their feeding patterns, or if they are solitary.
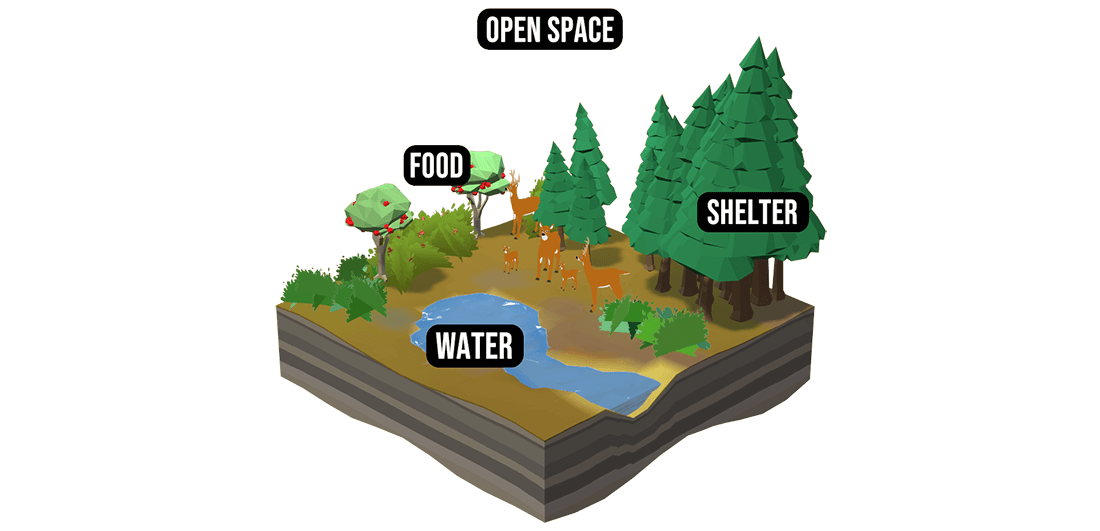
6. Habitat and range
Wild animals require five basic habitat components: food, water, cover, space and arrangement. The suitability for different vegetation groups or habitat elements will influence the types of wildlife that can survive in an area.
Protected Wildlife
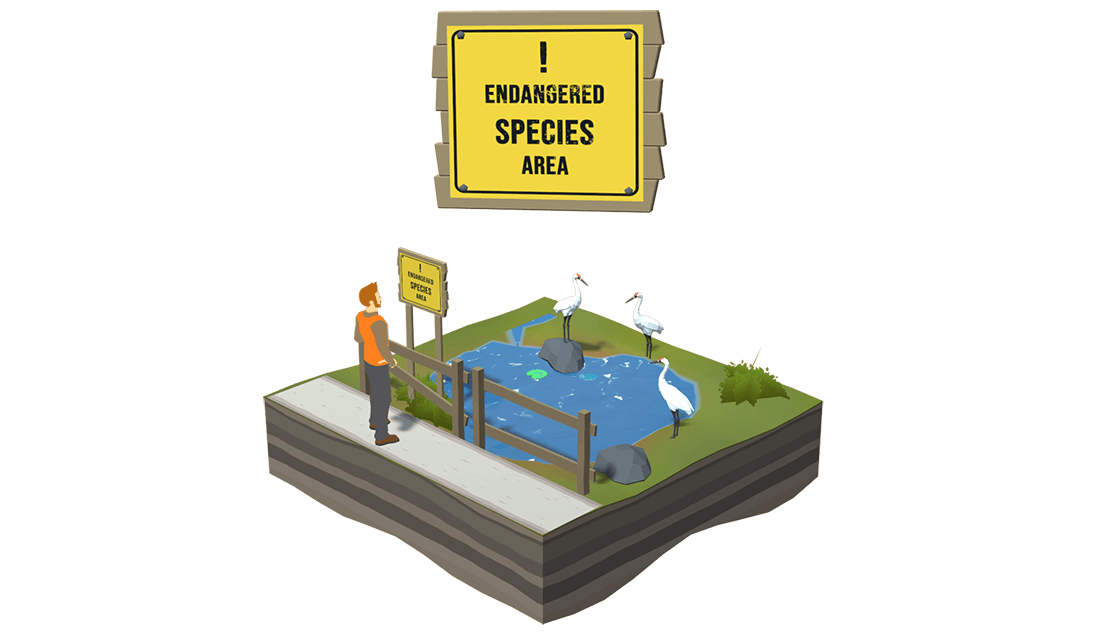
Some wildlife species are protected from being harvested because their population levels are very low. It is essential that all hunters be able to identify protected species that may be threatened or endangered.
Extinct means that a species no longer exists. A species that is in danger of extinction is said to be endangered. A species that is likely to become endangered in the near future is said to be threatened.